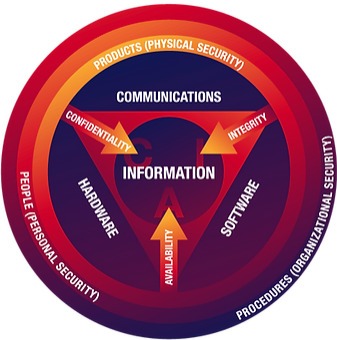
Here at BTI we have a team of experts available to assist you with all your IT, communication, and security needs. Do you want to have the highest security standards available for your company while also reducing costs and increasing your revenue? Contact us now or schedule a free consultation!
Menu
Close
- Commercial Security
IP Camera Solution Partners
Partners
Video Management
Surveillance Video Management Partners
- Alarm.com
- Arcules
- Axis Camera Station
- Avigilon
- Avigilon Alta
- Bosch
- Eagle Eye Networks
- Exacqvision
- Meraki
- Milestone
Partners
- Alarm.com
- Bosch Alarms
- DSC
- Honeywell
Key Features
- Gunshot Detection
- Flood & Leak Detection
- Crowd Density & Movement Analytics
- and more...
Industries Served
- Healthcare
- Logistics
- Government
- Education
- Manufacturing
- Transportation
- Public Utilities
- Entertainment
- Communication Products & Services
Communication Systems
Partners
Key Features
- Vendor-Agnostic Approach
- Comprehensive Integration
- IntelePeer
Key Features
- 4G & 5G Signal Boosting
- Multi-Carrier Support
- Indoor & Outdoor Boosting
Key Features
- Carrier-Neutral Approach
- VoIP, SIP Trunking & PRI Services
- Wireless & Mobility Solutions
- Contract Negotiation & Cost Optimization
- Cloud & Hybrid Deployment Options
Industries Served
- Healthcare
- Logistics
- Government
- Education
- Manufacturing
- Transportation
- Public Utilities
- Entertainment
- IT Products & Services
Top Services
- Managed IT Services
- Cybersecurity Services
- IT Helpdesk Services
- On-Site IT Support
- Network Design
- Network Installation
- Commercial Wi-Fi Installer
- Outsourced IT Services
- IT Hardware Maintenance
- IT Consultancy Services
- IT Infrastructure Services
- Camera, Access Control, & Alarm (Electronic Security)
- Managed WAN & SD-WAN
- Microsoft Tier 1 Partner
- Microsoft Teams Communication Partner
- Cisco Select Partner
- Cisco Meraki
- ConnectWise
- Kaseya/Datto
- Barracuda
- SonicWALL
- Dell
- HP
- Kemp
- SentinalOne
- Bitdefender™
Cloud Solution Providers
- Azure Solution Architech
- Microsoft 365
- Cloud Communication Solutions
- Cloud Contact Center Solutions
- Cloud Managed Network
- Cloud Security & Alarm Solutions
- Data Center/Private Cloud
Industries Served
- Healthcare
- Logistics
- Government
- Education
- Manufacturing
- Transportation
- Public Utilities
- Entertainment
- Industries
- Support
- About
- Contact
Locations

Call
Serving the Chicago metropolitan area, BTI Communications Group delivers comprehensive solutions in:

Call
Serving the Greater Los Angeles area, BTI Communications Group delivers comprehensive solutions in:

Call
Serving the Phoenix & Tucson metropolitan areas, BTI Communications Group delivers comprehensive solutions in:
Let’s talk about how BTI Communications Group can help your business stay secure, connected, and supported.